...
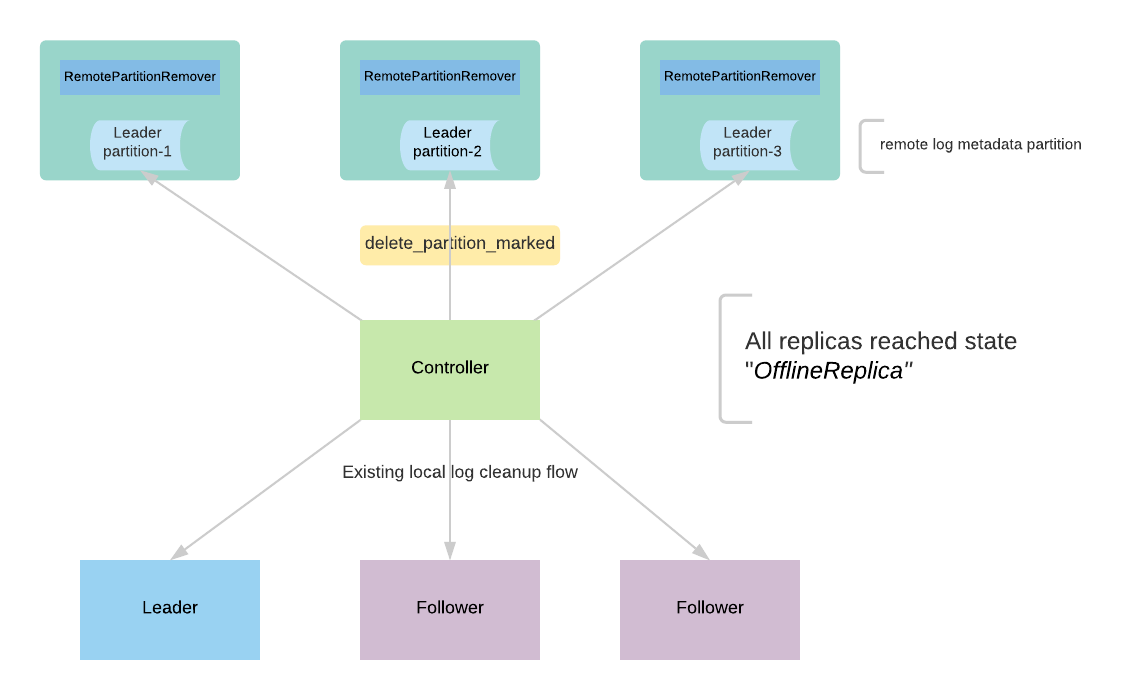
The controller receives a delete request for a topic. It goes through the existing protocol of deletion and it makes all the replicas offline to stop taking any fetch requests. After all the replicas reach the offline state, the controller publishes an event to the remote log metadata topic RemoteLogMetadataManager(RLMM) by marking the topic as deleted using RemoteLogMetadataManager.updateDeletePartitionState with the state as RemotePartitionDeleteState#DELETE_PARTITION_MARKED. With KIP-516, topics are represented with uuid, and topics can be deleted asynchronously. This allows the remote logs can be garbage collected later by publishing the deletion marker into the remote log metadata topic. RLMM is responsible for asynchronously deleting all the remote log segments of a partition after receiving RemotePartitionDeleteState as DELETE_PARTITION_MARKED.
Default RLMM handles the remote partition deletion by using RemotePartitionRemover(RPRM).
RPRM instance is created on a broker with the leaders of the remote log segment metadata topic partitions. This task is responsible for removing remote storage of the topics marked for deletion. It consumes messages from those partitions remote log metadata partitions and filters the delete partition events which need to be processed. It collects those partitions and executes deletion of the respective segments using RemoteStorageManager. This is done at regular intervals of remote.partition.remover.task.interval.ms (default value of 1hr). It commits the processed offsets of metadata partitions once the deletions are executed successfully. This will also be helpful to handle leader failovers to a different replica so that it can start processing the messages where it left off.
RemotePartitionRemover(RPRM) processes the request with the following flow as mentioned in the below diagram.
- The controller publishes deletepublishes DELETE_partitionPARTITION_marked MARKED event to say that the partition is marked for deletion. There can be multiple events published when the controller restarts or failover and this event will be deduplicated by RPRM.
- RPRM receives the deletethe DELETE_partitionPARTITION_marked MARKED and processes it if it is not yet processed earlier.
- RPRM publishes an event deleteevent DELETE_partitionPARTITION_started STARTED that indicates the partition deletion has already been started.
- RPRM gets all the remote log segments for the partition using RLMM and each of these remote log segments is deleted with the next steps.RLMM subscribes to the local remote log metadata partitions and it will have the segment metadata of all the user topic partitions associated with that remote log metadata partition.
- Publish deletePublish DELETE_segmentSEGMENT_started STARTED event with the segment id.
- RPRM deletes the segment using RSM
- Publish deletePublish DELETE_segmentSEGMENT_finished FINISHED event with segment id once it is successful.
- Publish deletePublish DELETE_partitionPARTITION_finished FINISHED once all the segments have been deleted successfully.
...
You can enable tiered storage by setting “remote.log.storage.enable” to true on the desired topics. . Before enabling tiered storage, you should make sure the producer snapshots are built for all the segments for that topic in all followers. You should wait till the log retention occurs for all the segments so that all the segments have producer snapshots. Because follower replicas for topics with tier storage enabled, need the respective producer snapshot for each segment for reconciliating the state as mentioned in earlier follower fetch protocol section.
Feature Test
Feature test cases and test results are documented in this google spreadsheet.
...