...
delegation.token.max.lifetime.sec : The token has a maximum lifetime beyond which it cannot be renewed any more. Default value 7 days.
delegation.token.expiry.time.sec : The token validity time in seconds before the token needs to be renewed. Default value 1 day.
delegation.token.master.key : Secret/masterKey to generate and verify delegation tokens. This masterKey needs to be configured with all the brokers.
Proposed Changes
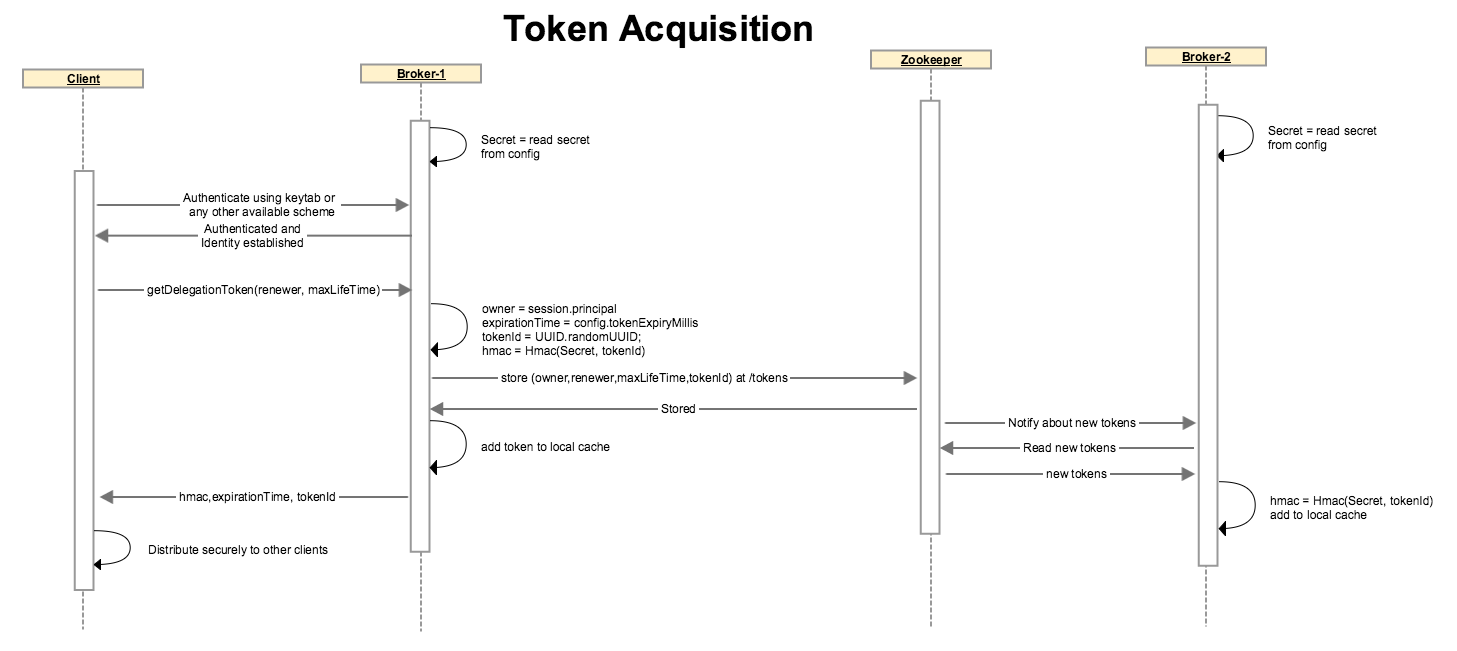
Token acquisition
Following steps describe how tokens can be acquired:
A (Admin/Delegation Token) client connects with one of the kafka broker. Client must be authenticated using any of the available secure channels so it must have a way to authenticate, i.e. Kerberos keytab or TGT.
Once a client is authenticated, it will make a broker side call to issue a delegation token. The request for delegation token will have to contain an optional renewer identity and max lifetime for token. The renewer is the user that is allowed to renew this token before the max lifetime expires. Renewer will default to the owner if not provided and Max life time will default to a server side config value (default days) Brokers will allow a token to be renewed until maxLifeTime but a token will still expire if not renewed by the expiry time. The expiry time will be a broker side configuration and will default to min (24 hours, maxlifeTime) . A Delegation Token request can be represented as class DelegationTokenRequest(renewer: Set[KafkaPrincipal], maxLifeTime: long). The owner is implicit in the request connection as the user who requested the delegation token.
The broker generates a shared secret based on HMAC-SASM(a Password/Secret shared between all brokers, randomly generated tokenId). We can represent a token as scala case class DelegationToken(owner: KafkaPrincipal, renewer: Set[KafkaPrincipal], maxLifeTime: long, id: String, hmac: String, expirationTime: long)
Broker stores this token in its in memory cache. Broker also stores the DelegationToken without the hmac in the zookeeper. As all brokers share the Password/Secret to generate the HMAC-SASM, they can read the request info from zookeeper , generate the hmac and store the delegation token in local cache.
All brokers will have a cache backed by zookeeper so they will all get notified whenever a new token is generated and they will update their local cache whenever token state changes.
Broker returns the token to Client. Client is expected to only make delegation token request over an encrypted channel so the token in encrypted over the wire.
Client is free to distribute this token to other Kafka clients (Producer/Consumers). It is the client’s responsibility to distribute the token securely.
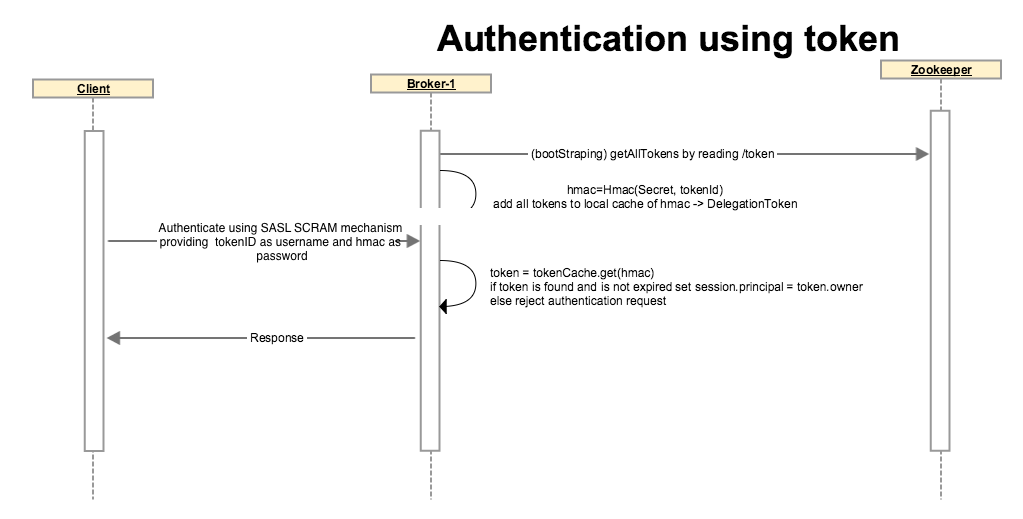
Authentication using Delegation Token
We will reuse the current SASL channel for delegation token based authentication.
SCRAM is a suitable mechanism for authentication using delegation tokens. KIP-84 proposes to support SASL SCRAM mechanisms. Kafka clients authenticate using SCRAM-SHA-256, providing the delegation token HMAC as password.
Server will look up the token from its token cache, if it finds a match and token is not expired it will authenticate the client and the identity will be established as the owner of the delegation token.
If the token is not matched or token is expired, broker throws appropriate exception back and does not allow the client to continue.
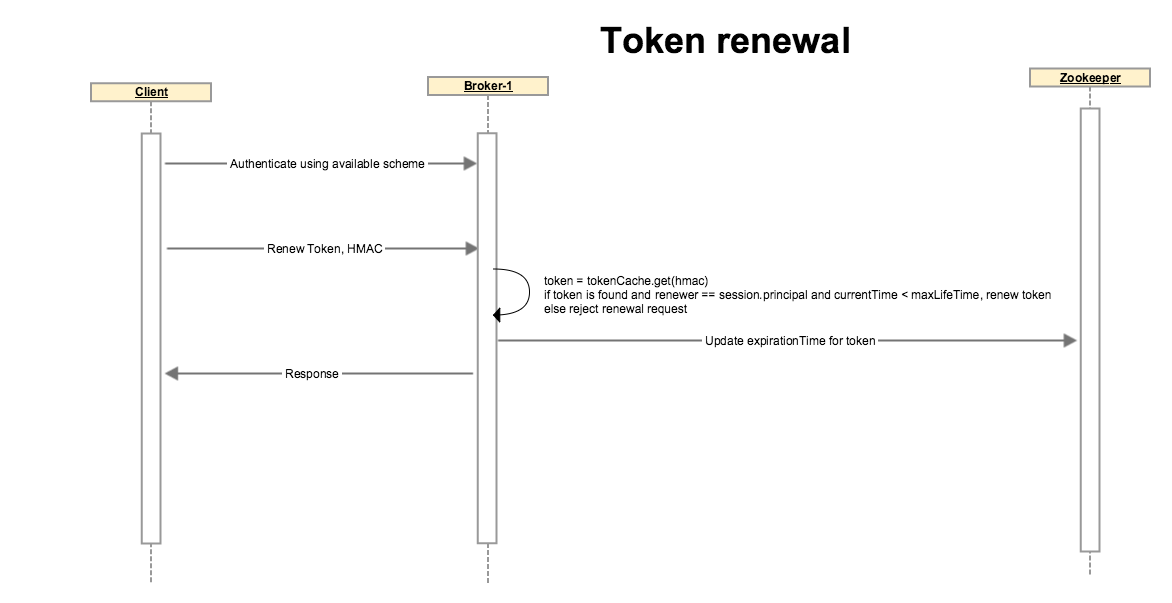
Token renewal
The (Admin/Delegation Token) client authenticates using Kerberos or any other available authentication scheme. A token can not be renewed if the initial authentication is done through delegation token, client must use a different auth scheme.
Client sends a request to renew a token with an optional renew life time which must be < max life time of token.
Broker looks up the token, if token is expired or if the renewer’s identity does not match with the token’s renewers, or if token renewal is beyond the Max life time of token, broker disallows the operation by throwing an appropriate exception.
If none of the above conditions are matched, broker updates token’s expiry. Note that the HMAC-SASM is unchanged so the token on client side is unchanged. Broker updates the expiration in its local cache and on zookeeper so other brokers also get notified and their cache statuses are updated as well.
Token expiration and cancellation
If a token is not renewed by the token’s expiration time or if token is beyond the max life time, it will be deleted from all broker caches as well as from zookeeper. Alternatively an owner or renewer can issue a expiration/cancellation by following a similar process as renewal.
Invalidating all tokens
In case of a password compromise scenario all the tokens can be deleted from zookeeper and this will result in all the tokens to be invalidated. We can provide a simple CLI tool for this.
Secret/Master Key
Secret/masterKey is used to generate and verify delegation tokens. This is supplied using config option. This masterKey needs to be configured with all the brokers. The current proposal does not support rotation of masterKey. We a requires a re-deployment when the masterKey needs to be rotated.
Token Details in Zookeeper
Token are stored in Zookeeper as properties in the path /tokenauth/tokens/<tokenUID>
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
// SCRAM credentials for tokenID token123: Zookeeper persistence path /tokens/token123
{
"version":1,
"owner" : "owner",
"renewer" : "renewer",
"maxLifeTime" : "maxLifeTime",
"tokenUID" : "tokenUID"
}; |
SCRAM Extensions
SCRAM messages have an optional extensions field which is a comma-separated list of key=value pairs.
After KIP-84 implementation , an extension will be added to the first client SCRAM message to indicate
that authentication is being requested for a delegation token. This will enable Kafka broker to obtain
credentials and principal using a different code path for delegation tokens.
DelegationToken Client
We will be providing a DelegationToken Client using which users can generate, renew and expire the tokens. This may part of AdminClient implementation (KIP-4).
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
public class DelegationTokenClient {
public TokenDetails generateToken(List<String> renewers, long maxLifeTime);
public boolean renewToken(bytes[] hmac, long expiryTime);
public boolean expireToken(bytes[] hmac, long expireTimeStamp);
public boolean invalidateToken(bytes[] hmac);
public void close();
} |
Command line tool
We will provide a CLI to acquire delegation tokens, renew tokens and to invalidate/expire tokens.
Changes to Java Clients (producer/consumer)
KIP-85 allows dynamic JAAS configuration for Kafka clients. After this we can easily configure the
delegation token for SCRAM-SHA-256 authentication.
...