...
Transactional
...
Client
...
Camel
...
recommends
...
supporting
...
the
...
...
...
from
...
the
...
...
...
using
...
spring transactions.
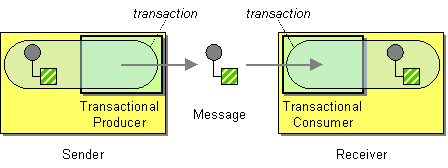
Transaction Oriented Endpoints (Camel Toes) like JMS support using a transaction for both inbound and outbound message exchanges. Endpoints that support transactions will participate in the current transaction context that they are called from.
You should use the SpringRouteBuilder to setup the routes since you will need to setup the spring context with the TransactionTemplates that will define the transaction manager configuration and policies.
For inbound endpoint to be transacted, they normally need to be configured to use a Spring PlatformTransactionManager. In the case of the JMS component, this can be done by looking it up in the spring context.
You first define needed object in the spring configuration.
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
transactions. !http://www.enterpriseintegrationpatterns.com/img/TransactionalClientSolution.gif! Transaction Oriented Endpoints ([Camel Toes|What is a Camel TOE]) like [JMS] support using a transaction for both inbound and outbound message exchanges. Endpoints that support transactions will participate in the current transaction context that they are called from. You should use the [SpringRouteBuilder|http://activemq.apache.org/camel/maven/camel-spring/apidocs/org/apache/camel/spring/SpringRouteBuilder.html] to setup the routes since you will need to setup the spring context with the [TransactionTemplate|http://www.springframework.org/docs/api/org/springframework/transaction/support/TransactionTemplate.html]s that will define the transaction manager configuration and policies. For inbound endpoint to be transacted, they normally need to be configured to use a Spring [PlatformTransactionManager|http://www.springframework.org/docs/api/org/springframework/transaction/PlatformTransactionManager.html]. In the case of the JMS component, this can be done by looking it up in the spring context. You first define needed object in the spring configuration. {code:xml} <bean id="jmsTransactionManager" class="org.springframework.jms.connection.JmsTransactionManager"> <property name="connectionFactory" ref="jmsConnectionFactory" /> </bean> <bean id="jmsConnectionFactory" class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory"> <property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://localhost:61616"/> </bean> {code} |
Then
...
you
...
look
...
them
...
up
...
and
...
use
...
them
...
to
...
create
...
the
...
JmsComponent.
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
{code:java} PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager = (PlatformTransactionManager) spring.getBean("jmsTransactionManager"); ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = (ConnectionFactory) spring.getBean("jmsConnectionFactory"); JmsComponent component = JmsComponent.jmsComponentTransacted(connectionFactory, transactionManager); component.getConfiguration().setConcurrentConsumers(1); ctx.addComponent("activemq", component); {code} h4. Transaction Policies Outbound endpoints will automatically enlist in the current transaction context. But what if you do not want your outbound endpoint to enlist in the same transaction as your inbound endpoint? The solution is to add a Transaction Policy to the processing route. You first have to define transaction policies that you will be using. The policies use a spring [TransactionTemplate|http://www.springframework.org/docs/api/org/springframework/transaction/support/TransactionTemplate.html] to declare the transaction demarcation use. So you will need to add something |
Transaction Policies
Outbound endpoints will automatically enlist in the current transaction context. But what if you do not want your outbound endpoint to enlist in the same transaction as your inbound endpoint? The solution is to add a Transaction Policy to the processing route. You first have to define transaction policies that you will be using. The policies use a spring TransactionTemplate to declare the transaction demarcation use. So you will need to add something like the following to your spring xml:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
like the following to your spring xml: {code:xml} <bean id="PROPAGATION_REQUIRED" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate"> <property name="transactionManager" ref="jmsTransactionManager"/> </bean> <bean id="PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate"> <property name="transactionManager" ref="jmsTransactionManager"/> <property name="propagationBehaviorName" value="PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED"/> </bean> <bean id="PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate"> <property name="transactionManager" ref="jmsTransactionManager"/> <property name="propagationBehaviorName" value="PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW"/> </bean> {code} |
Then
...
in
...
your
...
...
,
...
you
...
just
...
need
...
to
...
create
...
new
...
SpringTransactionPolicy
...
objects
...
for
...
each
...
of
...
the
...
templates.
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
{code:java} public void configure() { ... Policy requried = new SpringTransactionPolicy(bean(TransactionTemplate.class, "PROPAGATION_REQUIRED")); Policy notsupported = new SpringTransactionPolicy(bean(TransactionTemplate.class, "PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED")); Policy requirenew = new SpringTransactionPolicy(bean(TransactionTemplate.class, "PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW")); ... } {code} Once |
Once created,
...
you
...
can
...
use
...
the
...
Policy
...
objects
...
in
...
your
...
processing
...
routes:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
{code:java} // Send to bar in a new transaction from("activemq:queue:foo").policy(requirenew).to("activemq:queue:bar"); // Send to bar without a transaction. from("activemq:queue:foo").policy(notsupported ).to("activemq:queue:bar"); {code} h3. Samples In this sample we want to ensure that two endpoints is under transaction control. These two endpoints inserts data into a database. The sample is in its full as a unit test: TODO insert link. First of all we setup the usual spring stuff in its configuration file. Here we have defined a DataSource to the HSQLDB and a most importantly the Spring DataSoruce TransactionManager that is doing the heavy lifting of ensuring our transactional policies. You are of course free to use any of the Spring based TransactionMananger, eg. if you are in a full blown J2EE container you could use JTA or the WebLogic or WebSphere specific managers. We use the required transaction policy that we define as the {PROPOGATION_REQUIRED} spring bean. And as last we have our book service bean that does the business logic and inserts data in the database as our core business logic. TODO: Snippet E1 In our Camel route that is Java DSL based we setup the transactional policy, wrapped as a Policy. TODO: Snippet E1 Then we are ready to define our Camel routes. We have two routes: 1 for success conditions, and 1 for a forced rollback condition. This is after all based on a unit test. TODO: Snippet E2 As its a unit test we need to setup the database and this is easily done with Spring JdbcTemplate TODO: Snippet E5 And our core business service, the book service, will accept any books except the Donkeys. TODO: Snippet E1 Then we are ready to fire the tests. First to commit condition: TODO: Snippet E3 And lastly the rollback condition since the 2nd book is a Donkey book: TODO: Snippet E4 h4. See Also * [JMS] {include:Using This Pattern} |
Database Sample
In this sample we want to ensure that two endpoints is under transaction control. These two endpoints inserts data into a database.
The sample is in its full as a unit test.
First of all we setup the usual spring stuff in its configuration file. Here we have defined a DataSource to the HSQLDB and a most importantly
the Spring DataSoruce TransactionManager that is doing the heavy lifting of ensuring our transactional policies. You are of course free to use any
of the Spring based TransactionMananger, eg. if you are in a full blown J2EE container you could use JTA or the WebLogic or WebSphere specific managers.
We use the required transaction policy that we define as the PROPOGATION_REQUIRED spring bean. And as last we have our book service bean that does the business logic
and inserts data in the database as our core business logic.
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{snippet:id=e1|lang=xml|url=activemq/camel/trunk/components/camel-spring/src/test/resources/org/apache/camel/spring/interceptor/transactionalClientDataSource.xml} |
In our Camel route that is Java DSL based we setup the transactional policy, wrapped as a Policy.
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{snippet:id=e1|lang=java|url=activemq/camel/trunk/components/camel-spring/src/test/java/org/apache/camel/spring/interceptor/TransactionalClientDataSourceTest.java} |
Then we are ready to define our Camel routes. We have two routes: 1 for success conditions, and 1 for a forced rollback condition.
This is after all based on a unit test.
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{snippet:id=e2|lang=java|url=activemq/camel/trunk/components/camel-spring/src/test/java/org/apache/camel/spring/interceptor/TransactionalClientDataSourceTest.java} |
As its a unit test we need to setup the database and this is easily done with Spring JdbcTemplate
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{snippet:id=e5|lang=java|url=activemq/camel/trunk/components/camel-spring/src/test/java/org/apache/camel/spring/interceptor/TransactionalClientDataSourceTest.java} |
And our core business service, the book service, will accept any books except the Donkeys.
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{snippet:id=e1|lang=java|url=activemq/camel/trunk/components/camel-spring/src/test/java/org/apache/camel/spring/interceptor/BookService.java} |
Then we are ready to fire the tests. First to commit condition:
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{snippet:id=e3|lang=java|url=activemq/camel/trunk/components/camel-spring/src/test/java/org/apache/camel/spring/interceptor/TransactionalClientDataSourceTest.java} |
And lastly the rollback condition since the 2nd book is a Donkey book:
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{snippet:id=e4|lang=java|url=activemq/camel/trunk/components/camel-spring/src/test/java/org/apache/camel/spring/interceptor/TransactionalClientDataSourceTest.java} |
See Also
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|