Disclaimer: These API are used internally by Ambari only. Ambari Metrics Service released with Ambari 2.0 and 2.1 does not support https or authentication for these internal metrics API.
Data structures
Source location for common data structures module: https://github.com/apache/ambari/tree/trunk/ambari-metrics/ambari-metrics-common/
...
Sending Metrics to AMS (POST)
Sending metrics to Ambari Metrics Service can be achieved through the following API call.
...
Connecting (POST) to <ambari-metrics-collector>:6188/ws/v1/timeline/metrics/ Http response: 200 OK
Fetching Metrics from AMS (GET)
Sample callGET http://<ambari-metrics-collector>:6188/ws/v1/timeline/metrics?metricNames=AMBARI_METRICS.SmokeTest.FakeMetric&appId=amssmoketestfake&hostname=<hostname>&precision=seconds&startTime=1432075838000&endTime=1432075959000
...
{"metrics": [ {"timestamp": 1432075898089, "metricname": "AMBARI_METRICS.SmokeTest.FakeMetric", "appid": "amssmoketestfake", "hostname": "ambari20-5.c.pramod-thangali.internal", "starttime": 1432075898000, "metrics": {"1432075898000": 0.963781711428, "1432075899000": 1432075898000 } } ] } |
Generic GET call format
http://<AMS_HOST>:6188/ws/v1/timeline/metrics?metricNames=<>&hostname=<>&appId=<>&startTime=<>&endTime=<>&precision=<>
Query Parameters Explanation
| Parameter | Optional/Mandatory | Explanation | Values it can take |
|---|---|---|---|
| metricNames | Mandatory | Comma separated list of metrics that are required. | disk_free,mem_free... etc |
| appId | Mandatory | The AppId that corresponds to the metricNames that were requested. Currently, only 1 AppId is required and allowed. | HOST/namenode/datanode/nimbus/hbase/kafka_broker/FLUME_HANDLER etc |
| hostname | Optional | Comma separated list of hostnames. When no specified, cluster aggregates are returned. | h1,h2..etc |
| startTime, endTime | Optional | Start and End time values. If not specified, the last data point of the metric is returned. | epoch times in seconds or milliseconds |
| precision | Optional | What precision the data needs to be returned. If not specified, the precision is calculated based on the time range requested (Table below) | SECONDS/MINUTES/DAYS/HOURS |
Precision query parameter (Default resolution)
Query Time range | Resolution of returned metrics | Comments |
|---|---|---|
Upto 2 hours | SECONDS |
|
2 hours - 1 day | MINUTES | 5 minute data |
1 day - 30 days | HOURS | 1 hour data |
> 30 days | DAYS | 1 day data |
Specifying Aggregate Functions
http://<AMS_HOST>:6188/ws/v1/timeline/metrics?metricNames=regionserver.Server.totalRequestCount._avg,regionserver.Server.writeRequestCount._max&appId=hbase&startTime=14000000&endTime=14200000
http://<AMS_HOST>:6188/ws/v1/timeline/metrics?metricNames=regionserver.Server.readRequestCount,regionserver.Server.writeRequestCount._max&appId=hbase&startTime=14000000&endTime=14200000
Specifying Post processing Functions
http://<AMS_HOST>:6188/ws/v1/timeline/metrics?metricNames=regionserver.Server.totalRequestCount._rate,regionserver.Server.writeRequestCount._diff&appId=hbase&startTime=14000000&endTime=14200000
http://<AMS_HOST>:6188/ws/v1/timeline/metrics?metricNames=regionserver.Server.readRequestCount._max._diff&appId=hbase&startTime=14000000&endTime=14200000
Specifying Wild Cards
Both metricNames and hostname take wildcard (%) values for a group of metric (or hosts). A query can have a combination of full metric names and names with wildcards also.
Examples
http://<AMS_HOST>:6188/ws/v1/timeline/metrics?metricNames=regionserver.Server.%&appId=hbase&startTime=14000000&endTime=14200000
http://<AMS_HOST>:6188/ws/v1/timeline/metrics?metricNames=regionserver.Server.%&hostname=abc.testdomain124.devlocal&appId=hbase&startTime=14000000&endTime=14200000
http://<AMS_HOST>:6188/ws/v1/timeline/metrics?metricNames=master.AssignmentManger.ritCount,regionserver.Server.%&hostname=abc.testdomain124.devlocal&appId=hbase&startTime=14000000&endTime=14200000
http://<AMS_HOST>:6188/ws/v1/timeline/metrics?metricNames=regionserver.Server.%&hostname=abc.testdomain12%.devlocal&appId=hbase&startTime=14000000&endTime=14200000
Downsampling
Example
http://<AMS_HOST>:6188/ws/v1/timeline/metrics?metricNames=regionserver.Server.totalRequestCount._max&hostname=abc.testdomain124.devlocal&appId=hbase&startTime=14000000&endTime=14200000&precision=MINUTES
The above query returns 5 minute data for the metric, where the data point value is the MAX of the values found in every 5 minute range.
AMS Metadata API
AMS has 2 metadata endpoints that are useful for finding out the set of metrics it received, as well as the topology of the cluster.
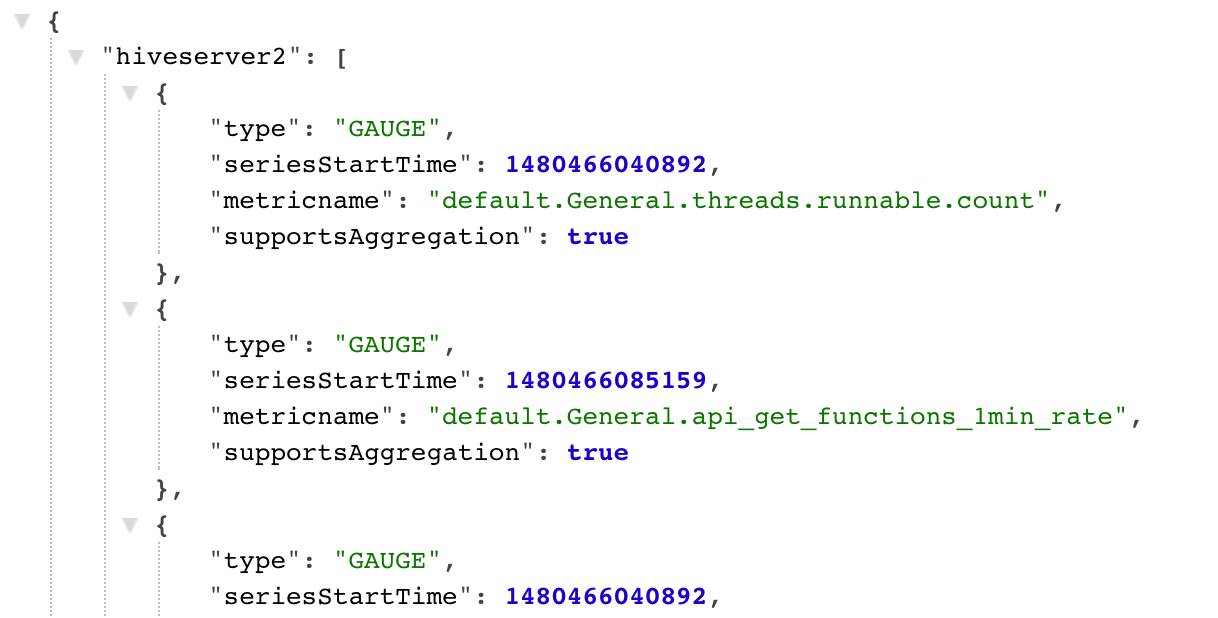
METRICS METADATA
Endpoint : http://<AMS_HOST>:6188/ws/v1/timeline/metrics/metadata
Data returned : A mapping between the set of APP_IDs to the list of metrics received with that AppId.
Sample data returned
HOSTS METADATA
Endpoint : http://<AMS_HOST>:6188/ws/v1/timeline/metrics/hosts
Data returned : A mapping between the hosts in the cluster and the set of APP_IDs on the host.
Sample data returned
Guide to writing your own Sink
- Include the ambari-metrics-common artifacts from source or maven-central (when available) into your project
- Find below helpful info regarding common data-structures to use from the ambari-metrics-common module
- Extend the org.apache.hadoop.metrics2.sink.timeline.AbstractTimelineMetricsSink class and implement the required methods
- Use the org.apache.hadoop.metrics2.sink.timeline.cache.TimelineMetricsCache to store intermediate data until it is time to send (example: collection interval = 10 seconds, send interval = 1 minute). The cache implementation provides the logic needed for buffering and local aggregation.
- Use org.apache.hadoop.metrics2.sink.timeline.AbstractTimelineMetricsSink#emitMetrics to send metrics to AMS backend.
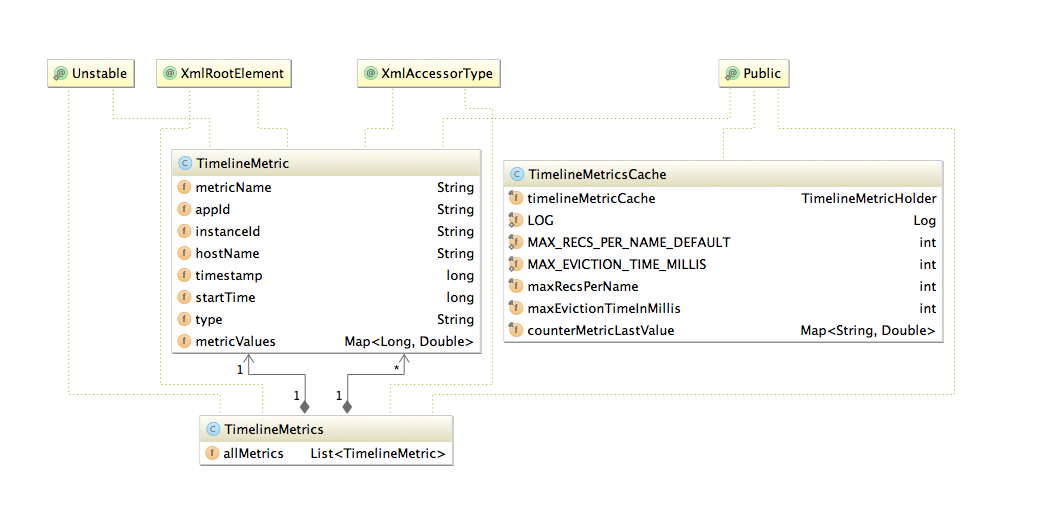
METRIC DATA STRUCTURE
Source location for common data structures module: https://github.com/apache/ambari/tree/trunk/ambari-metrics/ambari-metrics-common/
Example sink implementation: https://github.com/apache/ambari/blob/trunk/ambari-metrics/ambari-metrics-hadoop-sink/
INTERNAL PHOENIX KEY STRUCTURE
The Metric Record Key
...
data structure is described below:
Aggregation
Property | Type | Comment | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|
Metric Name | String | First key part, important consideration while querying from HFile storage | N |
Hostname | String | Second key part | N |
Server time | Long | Timestamp on server when first metric write request was received | N |
Application Id | String | Uniquely identify service | N |
Instance Id | String | Second key part to identify instance/ component | Y |
Start time | Long | Start of the timeseries data |
Precision query parameter
&precision=[ seconds, minute, hour, day ]
- This flag can override which table gets queried and hence influence the amount of data returned.
All API calls honor a query limit set in the Collector service configs.
...
Query Time range
...
Resolution of returned metrics
...
Comments
...
Last 1 hour
...
1 min aggregates
...
Precision data available on demand as well
...
Last 4 hours
...
30 sec resolution for 1 hour of data, 1 min aggregates thereafter
...
Last 10 hours
...
1 min aggregates
...
Honor query result limit
...
Last 24 hours
...
1 hour aggregates
...
min and seconds precision available if requested
...
Last week
...
1 hour aggregates
...
Last year
...
Daily aggregates
...
If query limit is reached query weekly aggregates
HOW AGGREGATION WORKS
- The granularity of aggregate data can be controlled by setting wake up interval for each of the aggregator threads.
- Presently we support 2 types of aggregators, HOST and APPLICATION with 3 time dimensions, per minute, per hour and per day.
...
- The HOST aggregates are just aggregates on precision data across the supported time dimensions.
- The APP aggregates are
...
- across appId. Note: We ignore instanceId for APP level aggregates. Same time dimensions apply for APP level aggregates.
- We also support HOST level metrics for APP, meaning you can expect a system metric example: "cpu_user"
...
- to be aggregated across datanodes, effectively calculating system metric for hosted apps.
- Each aggregator performs checkpointing by storing last successful time of completion in a file. If the checkpoint is too old, the aggregators will discard checkpoint and aggregate data for the configured interval, meaning data in
...
- between (now - interval)
...
- time.
- Refer
...
...
- for details of tables and records.