| Table of Contents |
|---|
1. Status
Current state: Under Discussion Accepted
Discussion thread: here
JIRA: here
...
The client rack awareness additions in partition assignments also affects how Kafka Streams can assign its tasks to clients so that cross rack traffic can be avoided as much as possible. This design discusses how we can augment current assignment logic in Kafka Streams to utilize rack information to minimize cross rack traffic with other constraints. Note the design doesn't change the rebalance protocol itself and only changes the assignment logic (read path in group leader in clients).
3. Current Task Assignment Logic
There are two assignors implemented in Kafka Streams now: StickyTaskAssignor and HighAvailabilityTaskAssignor. HighAvailabilityTaskAssignor was created for KIP-441: Smooth Scaling Out for Kafka Streams and and it’s the currently default assignor configured in Kafka Streams. As a result, this design will only augment HighAvailabilityTaskAssignor to account for the rack aware assignment. StickyTaskAssignor users who would like to use rack aware assignment should upgrade their Kafka Streams version to the version in which HighAvailabilityTaskAssignor and rack awareness assignment are availableStickyTaskAssignor can also be used by existing customer. We could put rack aware assignment logic in a separate module which be used by both StickyTaskAssignor and HighAvailabilityTaskAssignor . Below we mainly discuss how it works with HighAvailabilityTaskAssignor. It works similar for StickyTaskAssignor.
How HighAvailabilityTaskAssignor (HAAssignor) works
...
Klein’s cycle canceling algorithm can solve the min-cost flow problem in O(E^2CUE^2 * M * U) time where C M is max cost and U is max capacity. In our particular case, U is 1 and C is at most 3 (A task can have at most 3 topics including changelog topic?). since a task can be assigned once to one client. M is related to the number of topic partitions a task can subscribe. So the algorithm runs in O(E^2ME^2) time for our case. Note E is |T| * N|C| where T is are the number of tasks and N is C are the number of clients. This is because each task can be assigned to any client; so there is an edge because every task to every client. In another word, the time complexity of the algorithm is O(T^2*N^2M * |T|^2 * |N|^2) . Below is a rough sketch of the algorithm:
...
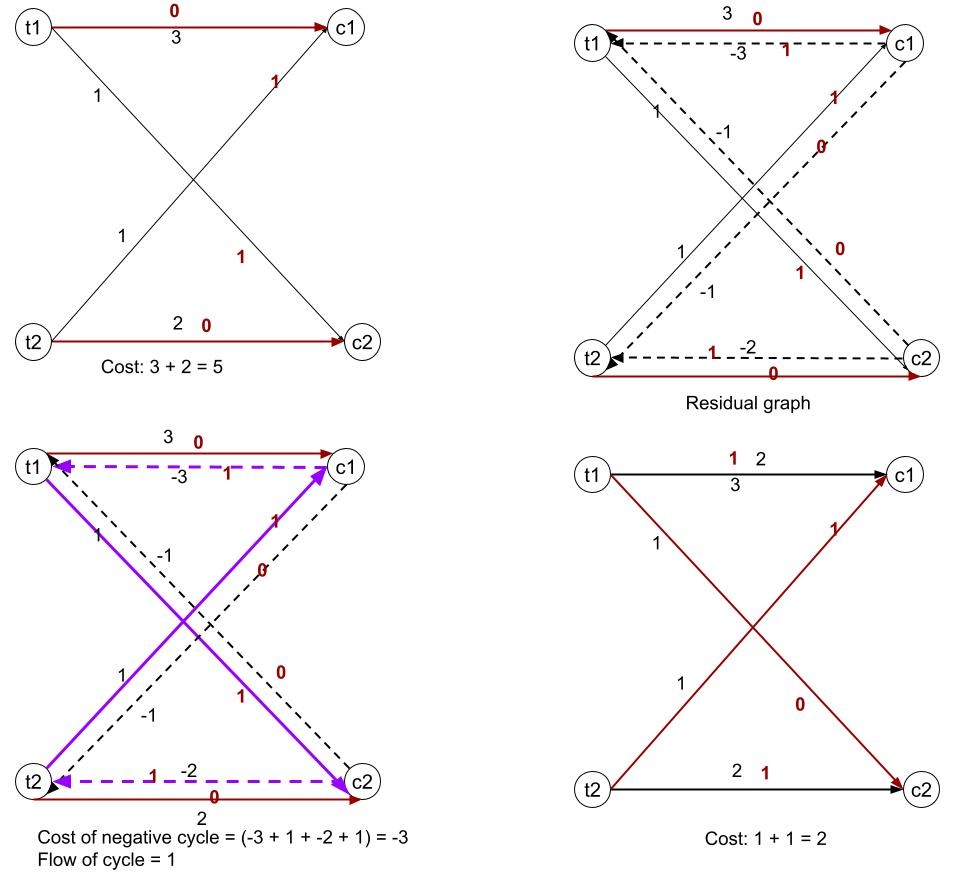
Negative cycles and residual graphs can be read here. Negative cycles can be found using Bellman-ford’s algorithm. How to find a feasible flow? It can be found by using step 1 - 2 of HAAssignor . What’s even nice about the cycle canceling algorithm is that since our graph is a bipartite graph, every time we find a negative cycle, the client nodes in the cycle satisfies that if there’s an in edge, there must be an out edge which means the flow of the clients won’t be changed. As a result, each round of the cycle canceling will reduce the cost and won’t change the total assignments of a client. So eventually, when there’s no more negative cycles, we find a min-cost balanced assignment. Below is an example of finding an min cost of 2 to assign task t1, t2 to clients c1, c2 .
B. Rack awareness assignment algorithm for active stateful tasks
I. Min cost with unbalanced sub-topology
...
One drawback of this solution is that the final solution is based on the number of tasks which can be assigned to each client computed from HAAssignor’s step 1 - 2. If every client has an equal number of threads but the number of tasks couldn’t be divided equally, then there’s one client with a different number of tasks. Ideally, this client could be anyone when we find our min cost assignment, but we fix it during our computation, which may result in a slight sub-optimal solution.
The runtime complexity of this algorithm is also higher since there are more edges in the graph. Suppose we have S sub-topologies, then we have (|T| + |T|*|C| + S*|C| + |C|) edges, which is still bounded by O(|T|*|C|) edges. So the time complexity is still O(M * T^2 * N^2) .
Since 4.B.I and 4.BSince 3.C.I and 3.C.II have different tradeoffs and work better in different workloads etc, we could add an internal configuration a config to choose one of them at runtime.
...
While the min-cost flow algorithm can find us assignments with min CRT cost, it’s also possible that if a TopicPartition ’s rack changes, the newly computed assignment could drastically change which can cause task shuffling and new warmups which involves more network and computation cost. So it’s preferable to make the new assignment as close to the old assignment as possible.
Option 1
It’s possible to assign costs to edges considering if the edge is in old assignment (based on John’s suggestion). This will help to make the new assignment overlap with old assignment especially when multiple min- cost solutions for CRT exist. The issue with this approach is that it’s impossible to make sure that the following probing rebalance can converge without remembering the computed target assignment and relevant clients/TopicPartition information. This stateful information makes the assignment logic much more complicated.
Option 2
. So it’s preferable to make the new assignment as close to the old assignment as possible.
While it's tempting to factor in previous assignment to make the new task assignment sticky, it While option 1 poses some challenges to store assignment information across rebalances and make sure the assignment can converge. Alternatively, we can choose to overlap more with target assignment computed by HAAssignor step 1 - 2. The idea is that if we always try to make it overlap as much with HAAssignor’s target assignment, at least there’s a higher chance that tasks won’t be shuffled a lot if the clients remain the same across rebalances even if some traffic cost changes. In this way, we can maintain a stateless assignment but at the same time try to overlap with some fixed assignment as much as possible. Below is the adjusted cost function suggested by John Roesler
...
TRAFFIC_WEIGHT and OVERLAP_WEIGHT indicate how much we favor minimizing traffic cost compared to maximizing overlap. In the extreme case, we can put OVERLAP_WEIGHT to 0 which means we always compute the lowest CRT assignment. We can expose these weights as internal configs. Note that we don't want to put a very high value for the weight because the cost upper bound appears in the algorithm's time complexity O(E^2 * (CUMU)) .
Summary
In summary, for active task assignment, we can add public configs such as rack.aware.assignment.strategy strategy with value min_cost cost or balanced_min_cost cost to choose algorithm I or algorithm II. We can make algorithm I as default to minimize total CRT cost. For cost computation, we can use Option 2 in III and expose configs to adjust the weight such as rack.aware.assignment.traffic_weight cost and rack.aware.assignment.non_overlap_weightnon_overlap_cost . For StickyTaskAssignor , we could run the same algorithm follow the active task assignment for stateful active tasks by adjusting the traffic_cost and non_overlap_cost to balance stickiness and traffic cost. Note that for StickyTaskAssignor , we would increase NON_OVERLAP_COST if t is not assigned to c in previous assignment.
C. Rack awareness assignment for standby tasks
...
| Code Block |
|---|
for (ClientState client : ClientStates) {
for (Task standby task : client.standbyTasks) {
for (ClientState otherClient : ClientState) {
if (client.equals(otherClient) || otherClient.contains(task)) {
continue;
}
for (Task otherStandbyTask : otherClient.standbyTask) {
if (swap task and otherStandbyTask is feasible and have smaller cost) {
swap(standbyTask, otherStandbyTask);
}
}
}
}
|
III. Summary
...
D. What if both rack information and rack aware tags are present
...
We can use a min-cost flow algorithm to assign stateless tasks. First, we can find a feasible solution based on task load. Then we can use the cycle canceling algorithm to compute minimum cost assignment as we do for active tasks. We can reuse the configuration for active tasks to control if we merely compute the min-cost assignment or we also balance tasks for the same sub-topology.
...
5. Public Interfaces
There will be a few new public configs added:
- rack.aware.assignment.strategy: this config controls if we should use 4.B.I or 4.B.II to compute min-cost with or without balanced sub-topologyrack.aware.assignment.enabled: this config controls if we should enable . If set to
NONE, rack aware assignment will be disabled - rack.aware.assignment.traffic_cost: this config controls the cost we add to cross rack traffic
- rack.aware.assignment.non_overlap_cost: this config controls the cost we add to non overlap assignment with targeted assignment computed by HAAssignor
Note client.rack consumer config needs to be configured by customer to enable rack aware assignment.
...
6. Compatibility, Deprecation, and Migration Plan
We will implement the new rack aware assignment logic in HighAvailabilityTaskAssignor and use the new assignor StickTaskAssignor. Rack aware assignment will be used only when
- client rack information appears in Subscriptions by configuring
client.rackon client side. If any client doesn't have rack information configured, a warning will be given and rack aware assignment will be disabled. - at least one of the TopicPartitions in some tasks have different cost compared to other TopicPartitions. This is because if all of
...
- them have the same cost, there's no point to use rack aware assignment logic to compute min cost since assigning tasks to any clients doesn't make a difference.
- rack.aware.assignment.enabled config is enabled
If users want to use rack aware assignment, they need to upgrade Kafka Streams to at least the earliest supported version. It's better to stop all the instances and start them all with the latest version with client.rack config, but it's also OK to do a rolling bounce with the new version. Rolling bounce with new version may cause the assignment changing between rack aware assignment and no rack aware assignment but eventually the assignment will be computed using rack awareness after every instance uses the new version.
...
7. Test Plan
- Unit test will be added for min-cost flow graph algorithm and rack aware assignment
- Existing integration test will be updated to ensure it works with or without rack configuration as well as with both
client.rackandrack.aware.assignment.tagsconfigurations - New integration test will be added to verify rack aware assignment
- Existing system test will be used to verify compatibility with old version
TaskAssignorConvergenceTestwill be updated to verify the new assignor will converge and it produces no worse assignment in terms of cross AZ cost- Performance test will be done manually to verify the efficiency of min-cost flow computation with large number of tasks and clients as well as different number of subscribed topic partitions
...
8. Rejected Alternatives
A. The follow algorithm for standby assignment is rejected
...