| Table of Contents |
|---|
Status
Current state: Under discussionAccepted
Discussion thread: here
JIRA: : KAFKA-1997
Released: 0.8.3
Please keep the discussion on the mailing list rather than commenting on the wiki (wiki discussions get unwieldy fast).
...
The Mirror Maker has a potential dataloss data loss issue as explained below:
...
The new mirror maker design is trying to solve the above issue as well as enhance the the mirror maker with the following features.
1.Currently Mirror Maker does not ensure the topics in source and target clusters have same partitions, which is required in many casesFiner control over the target partition.
2.Sometimes it is useful for Mirror Maker to Allow user do some simple process on messages (filter, message format change, etc.)of messages with a wired in message handler.
The new mirror maker is designed based on new consumer.
Public Interfaces
The no data loss solution uses the callback of new producer to determine the offsets to be committed.For Mirror Maker, an following interface change will be made to mirror maker.
- --consumer.rebalance.listener - to allow user to wire in a custom rebalance listener which implements ConusmerRebalanceCallback interface. An internal rebalance listener which implements ConsumerRebalanceCallback is wired in by default to avoid duplicates on consumer rebalance. User could still specify a custom listener class in command line argument. The internal rebalance listener will call that custom listener after it finishes the default logic.
...
- --
...
- consumer.rebalance.listener.args - to provide arguments to custom rebalance listener constructor.
- --message.handler - to allow user do some simple process on the messages (e.g. filtering, reformatting, etc)
- --message.handler.args - to provide arguments for message handler init() function.
- --abort.on.send.fail - define whether mirror maker should abort when a send failed(turned on by default)
Proposed Changes
Proposed Changes
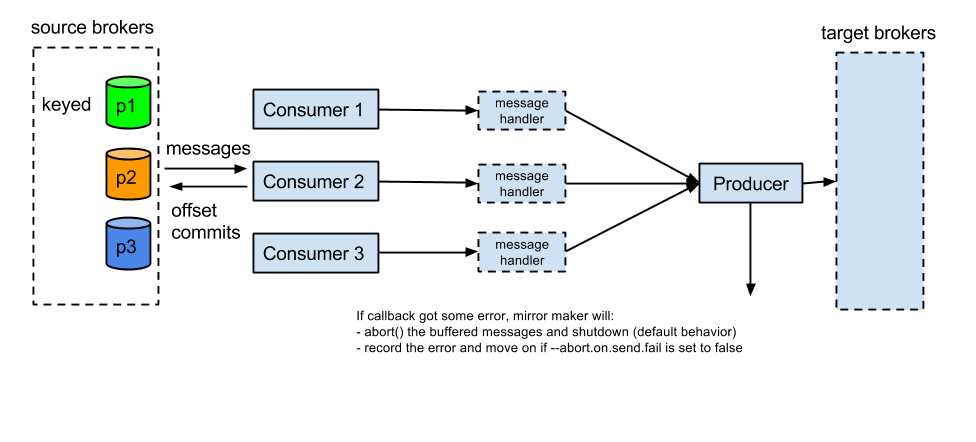
- Each mirror maker thread consume messages, process them and then send them.
- Scale by creating more mirror maker thread.
Each mirror maker thread has a consumer instance associated with it, the thread will be responsible for decompression, message handling, compression and offset commit. All mirror maker threads share a producer.
The only source of truth for offsets is target cluster. The offsets should only be committed after having received the confirmation from the target cluster. For the new producer, the confirmation is the ACK from target cluster.In that sense the consumer's offsets auto-commits should be turned off, and the offsets will be committed after a future associated with a message is received.
Whether message handler will be added is still under discussion. The benefit is that with this small add-on, user can chose to do some work such as filtering/reformatting in the pipeline once rather than do that in each client for multiple times. The downside of adding the message handler is that it is more or less an addition to the basic mirror maker function.
Offset commit
Each mirror maker thread maintains the consumer offsets for the partitions they are consuming from and commit the offsets periodically. Because the consumer offset is committed per SourcePartition/ConsumerGroup. A Map[TopicPartition, UnackedOffsetList] will be needed to track the offsets that is ready for commit.
Theoretically, we can just use a Map[SourceTopicPartition/TargetTopicPartition, AckedOffset], but in some scenarios, that might not work well. For example, if we have messages 1,2,3,4,5 from a source partition 1, message 1,2,4,5 are produced to destination partition 1, and message 3 is produced to destination partition 2. If we just use a Map[SourceTopicPartition/TargetTopicPartition, AckedOffset], it would hold { [(SourceTopicPartition=1, TargetTopicParitition=1),5], [(SourceTopicPartition=1, TargetTopicParitition=2),3] }. From the map itself, we cannot tell whether message 4 has been acked or not. And if there is no more message sent to target partition 2, the offset for source partition 1 will block on 3 forever.
periodically following a flush() call on producer.
The mirror maker thread logic is as below.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
while (!shutdown) {
val records = consumer.poll(timeout)
for (record <- records) {
val handledRecords = messageHandler.handle(record)
handledRecords.forEach(producer.send)
}
if (System.currentMilliSeconds - lastOffsetCommitMs > offsetCommitIntervalMs) {
producer.flush()
consumer.commitOffsets()
}
} |
Offset commit
Each mirror maker thread periodically flush() all the messages in producer and then commit offsetsThe UnackedOffsetList is a raw linked list that keep the messages offsets per source partition in the same order as they are sent by producer. An offset will be removed from the list when its ack is received. The offset commit thread always commit the smallest offset in the list (which is not acked yet).
No data loss option
A no data loss option is provided with the following settings, and these are also default settings:
- For consumer: auto.commit.enabled=false
- For producer:
- max.in.flight.requests.per.connection=1
- retries=Int.MaxValue
- acks=-1
- block.on.buffer.full=true
- set --abortOnSendFail
The following actions will be taken by mirror maker:
- Mirror maker will only send one request to a broker at any given point.
- If any exception is caught in producer/consumer thread or OutOfMemory exception is caught in offset commit mirror maker thread, mirror maker will try to commit the acked offsets then exit immediately.
- For RetriableException in producer, producer will retry indefinitely. If retry did not work, eventually the entire mirror maker will block on producer buffer full.
- For None-retriable exception, if --abort.on.send.fail is specified, stop the mirror maker. Otherwise producer callback will record the message that was not successfully sent but let the mirror maker move on. In this case, that message will be lost in target cluster.
...
A new consumerRebalanceListener needs to be added to make sure there is no duplicates when consumer rebalance occurs.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/** * This listener is used for execution of tasks defined by user when a consumer rebalance * occurs in {@link kafka.consumer.ZookeeperConsumerConnector} */ public interface ConsumerRebalanceListener { /** * This method is called after all the fetcher threads are stopped but before the * ownership of partitions are released. Depending on whether auto offset commit is * enabled or not, offsets may or may not have been committed. * This listener is initially added to prevent duplicate messages on consumer rebalance * in mirror maker, where offset auto commit is disabled to prevent data loss. It could * also be used in more general cases. */ public void beforeReleasingPartitions(Map<String, Set<Integer>> partitionOwnership); /** * This method is called after the new partition assignment is finished but before fetcher * threads start. A map of new global partition assignment is passed in as parameter. * @param consumerIdString The consumer instance invoking this rebalance callback * @param partitionAssignment The partition assignment result of current rebalance */ public void beforeStartingFetchers(String consumerIdString, Map<String, Map<Integer, ConsumerThreadId>> partitionAssignment); } |
The callback beforeReleasingPartitions will be invoked on consumer rebalance. It should
1. wait until the producer drains all remaining messagescall producer.flush
2. commit the offsets
Ensure same partition number in source and target topics
Each consumer will have a local topic cache that records the topics it has ever seen.
When new topic is created in source cluster, consumer rebalance will be triggered. In the ConsumerRebalanceCallback:onPartitionAssigned:
For consumer that consumes partition 0 of a topic:
- Check the topic in both source and target cluster to see if it is a new topic.
- If new topic is detected, create the topic with the same partition number in target cluster as in source cluster
For consumers that saw topics that does not exist in local topic cache:
- Wait until the topic is seen on target cluster.
When a partition expansion occurs, consumer rebalance will also be triggered. Above approach does not take care of this case.
The default rebalance listener does not do anything in beforeStartingFetchers callback. This callback could be useful in some cases, for example, to create a topic in the target cluster with the same number of partitions as in source cluster.
Message handler in consumer thread
...
public interface MirrorMakerMessageHandler { /** * Initialize the custom message handler with passed in arguments. This function will be called when mirror maker instantiate the custom message handler.
*/
public void init(String args);
/** * The message handler will be executed to handle messages in mirror maker * thread before the messages are handed to producer. The message handler should * not block and should handle all the exceptions by itself. */ public List<MirrorMakerRecord> List<ProducerRecord> handle(MirrorMakerRecord ConsumerRecord record);}...