You are viewing an old version of this page. View the current version.
Compare with Current
View Page History
« Previous
Version 10
Next »
Introduction
This tutorial covers running Nutch jobs on Apache Tez (instead of MapReduce).
Audience
This tutorial will appeal to Nutch administrators looking to improve runtime speed whilst maintaining MapReduce’s ability to scale to petabytes of data. Readers are encouraged to share their experienced using Nutch on Tez.
What is Apache Tez?
Apache Tez is described as an application framework which allows for a complex directed-acyclic-graph (DAG) of tasks for processing data. It is currently built atop Apache Hadoop YARN.
The 2 main design themes for Tez are:
- Empowering end users by:
- Expressive dataflow definition APIs
- Flexible Input-Processor-Output runtime model
- Data type agnostic
- Simplifying deployment
- Execution Performance
- Performance gains over Map Reduce
- Optimal resource management
- Plan reconfiguration at runtime
- Dynamic physical data flow decisions
By allowing projects like Apache Hive and Apache Pig to run a complex DAG of tasks, Tez can be used to process data, that earlier took multiple MR jobs, now in a single Tez job as shown below.
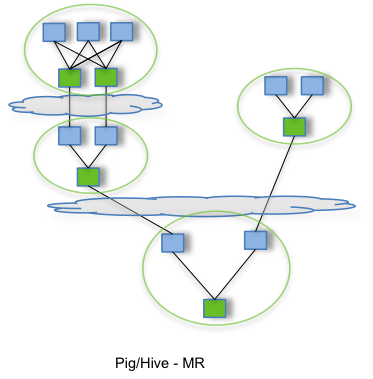
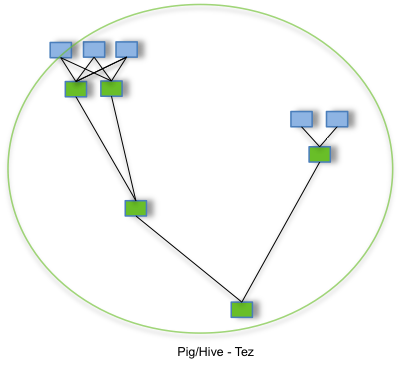
Configuring and Deploying Hadoop Services
Hadoop was configured and deployed in pseudo-distributed mode. The following assumes that you have already established a pseudo-distributed cluster and will make the following configuration changes before launching the new cluster.
<configuration>
<!-- Site specific YARN configuration properties -->
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name>
<value>mapreduce_shuffle</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.env-whitelist</name>
<value>JAVA_HOME,HADOOP_COMMON_HOME,HADOOP_HDFS_HOME,HADOOP_CONF_DIR,CLASSPATH_PREPEND_DISTCACHE,HADOOP_YARN_HOME,HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb</name>
<value>8000</value>
<description>Amount of physical memory, in MB, that can be allocated for containers.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb</name>
<value>500</value>
</property>
<property>
<description>Indicate to clients whether Timeline service is enabled or not.
If enabled, the TimelineClient library used by end-users will post entities
and events to the Timeline server.</description>
<name>yarn.timeline-service.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property>
<description>The hostname of the Timeline service web application.</description>
<name>yarn.timeline-service.hostname</name>
<value>localhost</value>
</property>
<property>
<description>Value must be the IP:PORT on which timeline server is running.</description>
<name>yarn.timeline-service.webapp.address</name>
<value>localhost:8188</value>
</property>
<property>
<description>Enables cross-origin support (CORS) for web services where
cross-origin web response headers are needed. For example, javascript making
a web services request to the timeline server.</description>
<name>yarn.timeline-service.http-cross-origin.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property>
<description>Publish YARN information to Timeline Server</description>
<name> yarn.resourcemanager.system-metrics-publisher.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
</configuration>
<configuration>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.framework.name</name>
<value>yarn-tez</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.application.classpath</name>
<value>$HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME/share/hadoop/mapreduce/*:$HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME/share/hadoop/mapreduce/lib/*</value>
</property>
</configuration>
export JAVA_HOME=/path/to/JDK
export HADOOP_HOME=/path/to/hadoop
export TEZ_JARS=/path/to/tez/tez-dist/target/tez-0.10.1-SNAPSHOT
export TEZ_CONF_DIR=/path/to/tez/conf
export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=$HADOOP_CLASSPATH:$TEZ_CONF_DIR:$TEZ_JARS/*:$TEZ_JARS/lib/*
You can then start all Hadoop services as follows
$HADOOP_HOME/sbin/start-dfs.sh
$HADOOP_HOME/sbin/start-yarn.sh
$HADOOP_HOME/bin/yarn --daemon start timelineserver
Configuring and Deploying Tez
First install Tez and ensure you can run the examples. Then progress to the following
hadoop fs -copyFromLocal tez/tez-dist/target/tez-0.10.1-SNAPSHOT.tar.gz /apps/tez-0.10.1-SNAPSHOT/
You can then evolve the tez-site.xml below
<configuration>
<property>
<name>tez.lib.uris</name>
<value>${fs.defaultFS}/apps/tez-0.10.1-SNAPSHOT/tez-0.10.1-SNAPSHOT.tar.gz#tez,${fs.defaultFS}/apps/nutch/apache-nutch-1.18-SNAPSHOT-bin.tar.gz#nutch</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>tez.lib.uris.classpath</name>
<value>./tez/tez-0.10.1-SNAPSHOT/*:./tez/tez-0.10.1-SNAPSHOT/lib/*:./nutch/apache-nutch-1.18-SNAPSHOT/*:./nutch/apache-nutch-1.18-SNAPSHOT/conf/*:./nutch/apache-nutch-1.18-SNAPSHOT/lib/*:./nutch/apache-nutch-1.18-SNAPSHOT/plugins/*/*</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>tez.use.cluster.hadoop-libs</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>plugin.folders</name>
<value>nutch/apache-nutch-1.18-SNAPSHOT/plugins</value>
</property>
<property>
<description>Enable Tez to use the Timeline Server for History Logging</description>
<name>tez.history.logging.service.class</name>
<value>org.apache.tez.dag.history.logging.ats.ATSHistoryLoggingService</value>
</property>
<property>
<description>URL for where the Tez UI is hosted</description>
<name>tez.tez-ui.history-url.base</name>
<value>http://localhost:8080/tez-ui-0.10.1-SNAPSHOT</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>tez.runtime.convert.user-payload.to.history-text</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
</configuration>
Configuring and Deploying Nutch
cd $NUTCH_HOME && ant clean tar-bin
hadoop fs -copyFromLocal dist/apache-nutch-1.18-SNAPSHOT-bin.tar.gz /apps/nutch-1.18-SNAPSHOT
You can then run Nutch jobs as usual e.g. nutch inject crawldb urls
The following content relates to ongoing experiments which have been run by members of the Nutch community.
Experiments
Running the Injector job on Tez

| Run # | YARN Engine | # of URLs | Elapsed Time |
|---|
| 1 | MapReduce | 11523 | 00:00:34 |
| 2 | MapReduce | 11523 | 00:00:32 |
| 3 | MapReduce | 11523 | 00:00:34 |
| 4 | Tez | 11523 | 00:00:42 |
| 5 | Tez | 11523 | 00:00:13 |
| 6 | Tez | 11523 | 00:00:14 |
| 7 | MapReduce | 15763469 | 00:03:21 |
| 8 | MapReduce | 15763469 | 00:03:13 |
| 9 | MapReduce | 15763469 | 00:02:38 |
| 10 | MapReduce | 15763469 | 00:02:37 |
| 11 | MapReduce | 15763469 | 00:02:48 |
| 12 | Tez | 15763469 | 00:02:14 |
| 13 | Tez | 15763469 | 00:02:10 |
| 14 | Tez | 15763469 | 00:02:13 |
From the above Tez clearly appears to offer significant runtime improvements over MapReduce. This is very promising however much more experimentation is required.
Observed Issues
When using Tez, counters are not populated. This makes sense as all existing counters are created using MapReduce framework Context objects. This presents a major issue. Counters are a requirement to have as they are key to regular inspections of ongoing crawls, finding errors and debugging. The org.apache.tez.common.counters package may offer a equivalent replacement but this has still to be investigated.


